Components
Click on the bubble to read more about each feature:
Data Collection
The data collection component provides secure electronic delivery of reports (UTRs, STRs, CTRs, and EFTRs from reporting entities using SSL 512-bit encryption. It allows the FIU to create (register) reporting entities in the system and then provides functionality for reporting entities to create and/or change contact details, upload reports, and perform data entry.
Reports can be submitted in the following three ways:
- Offline through XML data exchange such as an e-mail attachment, CD, HD, etc.
- Online through direct upload of XML data messages
- Online through forms which are filled in and submitted on the FIU's secure goAML website.
Report formats are defined in the collection component. If reports are submitted to the FIU on paper, these can be entered manually by the FIU. Additional data requested by the FIU (bank statements, account opening details etc.) can also be submitted both online or through offline media.
goAML Web provides a secure web-based interface for communication between the FIU and its reporting entities. It facilitates the submission of reports to the FIU via automated XML file upload, online report forms, or the sending of XML files as attachments by secure email. The communication function can be used to provide information to reporting entities individually or on a collective basis. It can also provide links to other related websites and a "Contact Us" link, if required. FIUs can also customize goAML Web to local requirements.
The reporting interface provides web-based forms that facilitate reporting multi-party transactions. This a particularly important feature for reporting entities such as dealers in high-value goods who tend to report single-sided transactions even when there are several parties to the transaction.
goAML Web also provides the Additional Information Report (AIR). Upon receipt of an STR or other report, an FIU will often need more information (particularly transaction histories) from the reporting institutions. AIR enables the automation of that process. Upon request, the reporting institution can compile the information in XML format and transmit it electronically to the FIU. The requested data is uploaded to the goAML database and is immediately available to analysts.
Data Clean Up
FIU personnel can view selected reports or all reports from reporting entities and manually accept or reject them.
Alternatively, the Data Clean Up component automatically checks incoming electronic data for completeness and accuracy (compliance with XML schema). This process takes place in a staging area outside the main system environment (the DMZ). If incoming data is correct and complete, it is transferred to the main database. If it is not, it is returned to the reporting entity for correction.
XML Rules Editor
An XML Rules Editor allows the creation of rules to accept or reject individual transactions in a report after XML validation. The Rules Editor provides flexibility in checking transactions details, as well as, the more rigid check against the schema. Syntax is a normal validation/check against schema. Symantix, which is defined by the user, checks transactions for pre-defined conditions such as non-alphabetical characters in names, age of transactor, etc. This tool permits the extraction of faulty transactions from a report and sends those transactions back to the reporting institution for correction or enquiry. The rest of the report is validated.
This activity is recorded by goAML to give the compliance staff of the FIU continuous and detailed information about who is reporting (and who isn't), what they are reporting, and the standard of the reports, etc. This data can be used to provide compliance reports on the reporting practices and standards of reporting entities as a whole, by business type, by geographical location, and/or as individuals, etc. This data can be charted to add visual weight to reports.
Subject Unification
Subject Unification is available after report and business rule validation to allow non-destructive subject promotion and demotion. This means that database objects can be merged when multiple entries relate to the same object. Conversely, an object can be separated into multiple objects when it is found that the original object has been incorrectly entered as a unique identity. Merging of objects can be done automatically based on user-defined rules. The original data always remains, and all activities are logged.
Virtual Object
When there is doubt whether two or more database entries (such as persons or entities) relate to the same identity, analysts can create a Virtual Object (database object) based on the assumption that two or more identities in the system are the same, but without merging those identities.
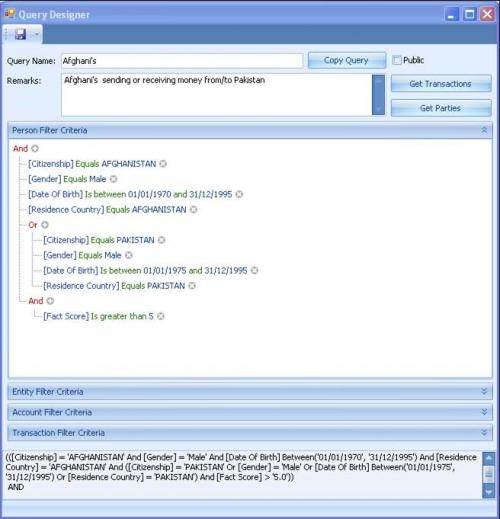
Ad Hoc Queries and Matching
The Ad Hoc Queries and Matching component allows users to enter requests for matches on a variety of criteria such as name, address, country, account number, identification document number or type, etc. Some search options are specific to the preferred search criteria and full details. However, partial details can also be entered.
Quick Finder
The Quick Finder allows the user to search the entire database. After the query is submitted, the system returns a list of all entities matching the requested criteria and links them if links exist.
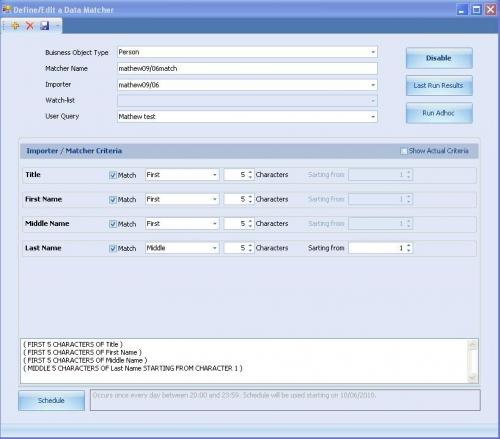
Data Matching Module
The Data Matching Module features an importer that can input data on persons, accounts and entities in any format from external sources and match this data against the FIU's report database. The data matching process can be run on an ad hoc basis. When it is run as a scheduled task at regular intervals, the matching process can automatically create analytical case proposals.
Statistical Reports
This component allows many types of statistical reports to be generated automatically or ad hoc statistics to be obtained from the system to prepare reports on all activities carried out in the goAML application. Statistical reports include a variety of compliance reports that track the numbers, types, values, etc. of the mandated reports collected by the FIU and identify the reporting entities by type, name, address etc. In addition, the FIU can analyze and report on its own activities for internal management or for more general consumption. The reports produced by this component of goAML can contain general or specific statistics of the FIU's performance overall or in specific areas of activity. These reports are of considerable assistance in compiling the FIU's annual report, in reporting to Parliament, responsible Ministers or Heads of Departments, or for identifying gaps or weaknesses in the FIU's performance that require addressing by adding extra resources, changes to work practices etc.
Structured Analysis (Strategic and Tactical)
This component is very feature-rich and covers the contents of all reports submitted to the FIU and any other data held in the FIU's database. Analysts can access the entire data set (if their roles and security clearances permit) for in-depth analysis at both the tactical and strategic levels. goAML provides a wide variety of analytical tools and views that allow analysts to look at data from numerous angles.
A variety of tools such as sorting, filtering, and pivoting are integrated into this component of goAML, allowing analysts to reveal patterns, anomalies, key variables, relationships, and much more using just one application. Trends and patterns in financial transactions of persons and entities, occupational types, geographical regions, etc. can be analyzed.
Tactical and Strategic Analysis
Tactical analysis on specific targets can be carried out utilizing the full content of the database, as well as, more general strategic analysis using all data contained in the database.
The strategic analysis function provides a wide range of options, including analysis pivoting on top players in terms of account or transaction activity, primary account holder, event timelines, signatories, account activity, transaction type, occupation, and much more.
Virtual Object
This feature allows analysts to create a Virtual Object (database object) based on an assumption that two or more identities in the system are the same. It also enables the grouping of identities under one object to create social network structures such as family associations and gang associations. All information relating to a Virtual Object will be retrieved when a query is run against an identity included in the Virtual Object.
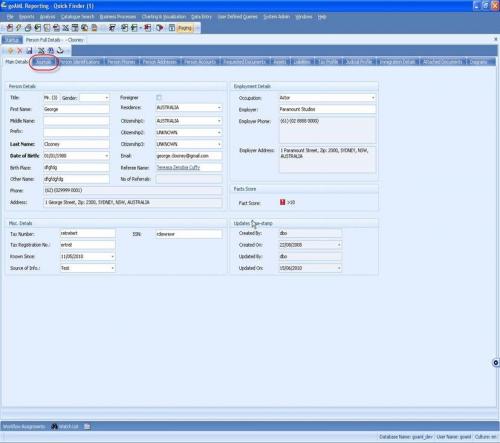
Profiling
Profiling is a powerful new tool that provides analysts (particularly strategic analysts) with a highly-flexible means by which to run queries and scenarios against part or all of the FIU's data holdings. Using the Profiling tool, analysts (individually or collectively) can create, save, and share their queries of the data based on any database object and according to their requirements. It looks and feels like a filter builder in Excel and allows an almost limitless range of questions to be put to the data set. These can range from the very simple and general to highly-detailed queries aimed at extracting very specific information from data holdings. Profile matches can be run as a "one off" query, saved for reuse as and when required, or set to run against the data holdings on a scheduled basis.
Rule-based Analysis
The Rule-based Analysis component of goAML is structured into three parts:
- The Rules Engine
- The Rules Editor
- The Alert Manager
The Rules Engine continuously scans the data in the goAML database looking for data that matches certain circumstances (rules) that have been deemed by the FIU as worthy of specific attention. The rules can consist of virtually any set of facts or circumstances such as a pattern of transactions by an account type, occupation type, a change in transaction frequency in a certain type of account, or commencement of cash deposits by a certain occupational type, and many more. There is no limit to the number and type of rules that can be applied.
The Rules Editor is a user interface that allows rules to be written and submitted to the Rules Engine by anyone in the FIU authorized to do so. Rules can be formulated by imposing conditions on standard intelligence objects such as persons, entities, and accounts in the much the same way as filters can be formulated in Excel and other analytical programs. The user does not need to write computer code, and the FIU can customize the submission and authorization process to suit its situation and work preferences.
The Alert Manager is for managing and prioritizing alerts triggered by the rules engine.
Workflow System
The Workflow System allows FIU management to set and maintain system-driven sequenced steps in the process of information management based on the FIU's standard operating procedures. This includes the receipt and processing of reports and other information; the end-to-end process of analysis; the management of information dissemination; and any feedback processes. This component drives the work of the FIU as it relates to receipt and management of information and the development and dissemination of intelligence. The Workflow System is fully customizable so that the workflow process can be tailored to the needs and processes of the FIU. While the Workflow System is programmed to follow a set step-by-step process, it is flexible enough to be overridden when circumstances (such as the urgency of a matter) dictate that the normal workflow process cannot be followed.
The Workflow System allows multiple workflows to reflect the standard operating procedures applied to different aspects of an FIU's business. The system allows separate workflow processes to be applied to different tasks and activities. For example, a workflow can be applied to the initial analysis of reports. However, if a report is escalated to a case proposal, a different workflow process might commence. If the matter is escalated further, another workflow process might drive the task to its conclusion. Each workflow is configurable to the requirements of the FIU.
The Workflow System can illustrate the workflow process by producing a diagram depicting the workflow steps. The diagram is automatically amended as the workflow process itself is amended. The system can produce a range of reports that give management statistical information or a snapshot of current tasks proceeding through the workflow stages.
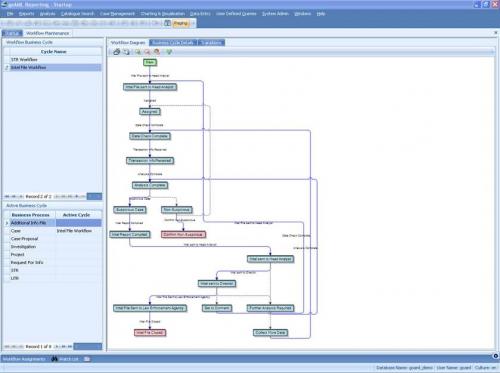
Task Assignment and Tracking
This component allows managers and supervisors to allocate tasks with or without pre-set time limits and to monitor and track the progress of that task or tasks as they progress through the workflow cycle. Whenever a new task is assigned or an existing task is re-assigned or becomes due, the person responsible for the task is advised in the goAML system itself and also by e-mail. The system also provides alerts to supervisors and managers when tasks are due or overdue or if tasks have been re-assigned, terminated, or if the standard workflow has been overridden for any reason. This component also provides management with valuable statistical information that measures the performance of the workflow process itself and of the various FIU personnel working in it.
Document Management (full-text search)
The Document Management component allows the capture of documents through electronic transfer and/or scanning and optical recognition. Documents can be recorded and filed according to a wide variety of document characteristics. When a new document enters the system, it is not simply recorded as an image. The text is lifted from the document and filed in the database like entered data so the entire content of the document is searchable and retrievable. The document can be retrieved at any time by clicking on links to it which appear in various lookup screens or by searching for key words or phrases in the document. A general text search will retrieve all documents containing that text or text that is similar to the query.
Intelligence File Management System
The Case Proposals component is the first step in the escalation process of the internal intelligence cycle for the FIU. This automated case building process can save many hours of analyst time. When an analyst has compiled all initial information, analyzed it, and a decision has been made that a matter under inquiry (whether originating from mandated reports or other sources) is worthy of further attention, the analyst can create a case proposal.
Moving data into the file automatically creates links in the file to all other data related to the original data. For example, if the analyst moves a name into the case proposal, all data in the goAML database related to that name (such as addresses, accounts, known transactions, linked associates, etc.) is automatically moved into the case proposal. All further work on this matter is then handled in the case proposal and any data added is automatically linked to the data in the case proposal and any other associated data in the database.
The practical implication of this is that the system adds most of the substance to the case proposal. Others within the FIU can access and contribute to the case proposal as it develops and its progress can be monitored by supervisors or management. At any point, the analyst can edit the case proposal to suit the matter under investigation.
Case proposals can also be automatically generated from the automated data matching process.
The entire Case File or selected parts of it can be disseminated as an intelligence package to law enforcement or other authorities. The usual next step in the analytical process is escalation from a Case Proposal to a Case File although the Case Proposal step can be omitted in favor of escalating the matter directly from analysis to a Case File.
Integration and/or Data Acquisition
goAML provides a variety of options that allow the FIU to request and collect data from any external source. The range of options can vary from the very high-tech to a letter delivered by post or by hand. At one end of the spectrum, goAML can be configured so that an analyst or other authorized person in the FIU can perform an online query of external databases to look for information associated with persons, entities, or others of interest to the FIU . This can be virtually any type of database hosted by any type of agency and can include criminal history records, vehicle registrations, company registrars, and more. The system can be configured to cluster such enquiries so that upon entry of the details of the person or entity in question, all the databases to which the FIU has access can be queried simultaneously.
Because of the diversity and numbers of databases and agencies that could be involved in this type of online query facility, this functionality has to be individually built for each installation. That build is not included in the routine goAML cost structure.
If this level of automation is not possible, requests for information can be transmitted in a less automated fashion. A standard request form can be configured in goAML and then populated by an analyst or other authorized person with data directly from the case or report being worked on. The request can be addressed from a pre-formatted list of agencies or organizations the FIU regularly queries or can be addressed manually for special cases. Multiple requests can be produced using the same set of data but addressed to different agencies or organizations. These requests can then be sent as e-mail attachments, faxes, or printed and posted or hand delivered. Whichever method is used, goAML provides the full functionality to produce and transmit the enquiry. So, there is no need for any other system. As a result, this saves much valuable analyst time.
Charting and Diagramming
The Charting and Diagramming tool is fully integrated into goAML. When activated by the analyst, it runs continuously and charts all analysis processes undertaken by the analyst. It is designed to allow FIUs to chart transactional flows and to show the connections of the parties to the transactions (persons, entities, accounts etc.) to the transactions themselves and to other connected persons, addresses, phone numbers, and more.
The analyst can manually switch between the charting tool and table data views or (if using two screens) can view both simultaneously. The staged drill-down function of the charting tool can drive the tactical analysis process by accessing data directly from the database and drawing flows, links, and associations automatically.
Alternatively, the analyst can use the tool to expand the chart and show flows and links one step at a time originating from accounts, persons, addresses, phone numbers, or any other available object. The analyst can also simply draw a chart without reference to the database. The analyst can use the diagram options and icons in this component to manually compile charts for individual cases.
Charts compiled in goAML are fully compatible with i2 Analyst Notebook©. So, if the FIU includes charts in its intelligence packages and the receiving agency is using i2 Analyst Notebook©, the chart from the FIU can be loaded to i2 Analyst Notebook© in the receiving agency and the chart can be further developed in the course of that agency's enquiries or investigations.
Intelligence Report Writer
The Intelligence Report Writer tool is a fully-integrated component that usually forms the final stage in the analytical process and provides a template and process for preparing the final intelligence package for dissemination to the FIU's end user agencies. The report can be customized to the FIU's specific requirements in terms of appearance and content. Like the intelligence file development component, the report can be populated entirely with data contained in the goAML system.
The report consists of a number of components including an executive summary, intelligence hypothesis, main report body, and conclusions. The person(s) preparing the report can (by checking or unchecking boxes) include or exclude any information when it is created. Documents, charts, and other items can be attached, and the report and all associated data can be disseminated in XML format, or the report body can be printed or sent as an e-mail attachment while the associated data can be converted to Excel workbooks and disseminated in that format. The Report Writer tool allows any type of report format to be created in the application and stored in the database including connectivity to other data sources.
